Squamous Metaplasia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Squamous metaplasia is a
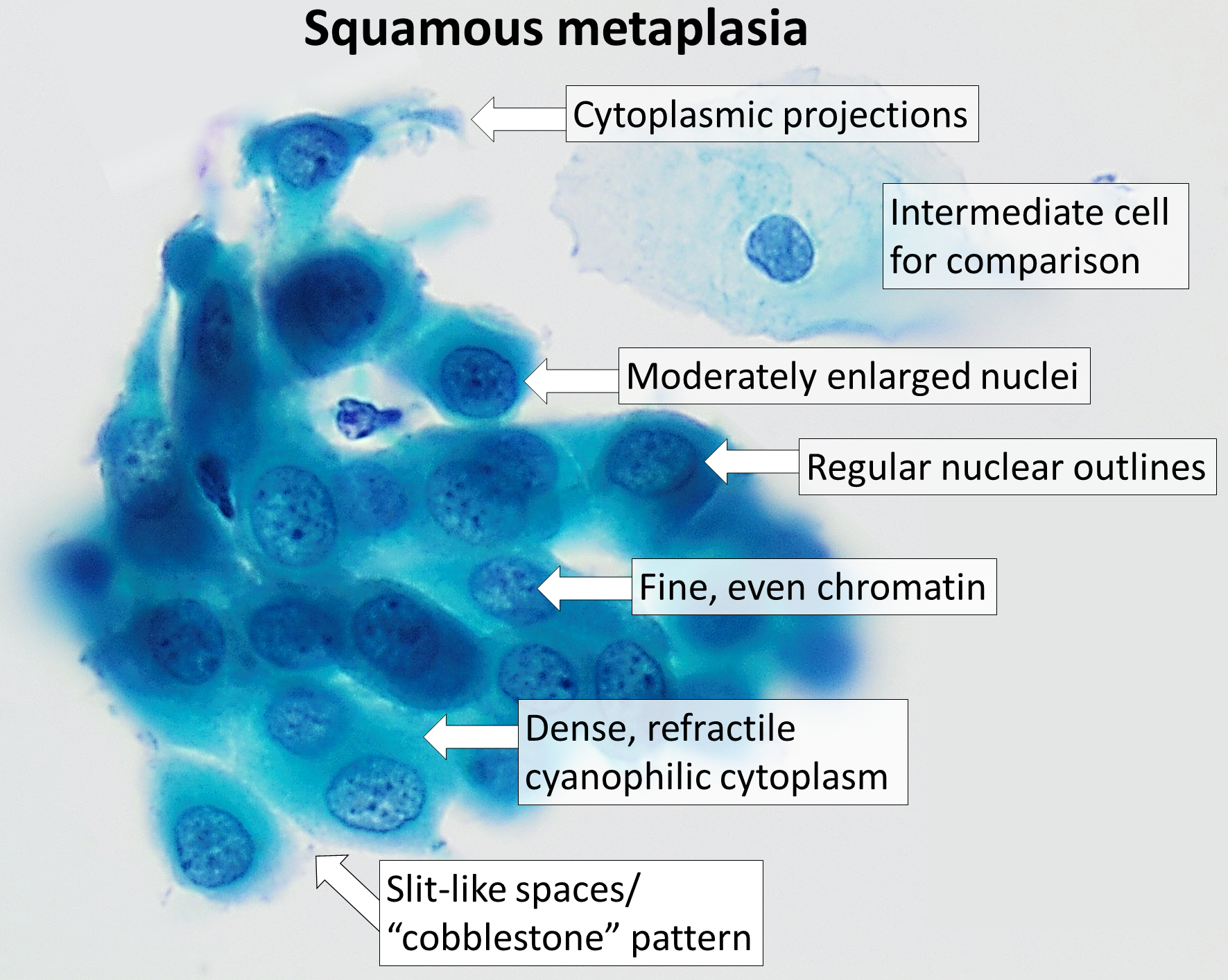 In regard to the cervix, squamous metaplasia can sometimes be found in the
In regard to the cervix, squamous metaplasia can sometimes be found in the
benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malign ...
non-cancerous change (metaplasia
Metaplasia ( gr, "change in form") is the transformation of one differentiated cell type to another differentiated cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abno ...
) of surfacing lining cells (epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
) to a squamous morphology.
Location
Common sites for squamous metaplasia include thebladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters ...
and cervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during ...
. Smokers often exhibit squamous metaplasia in the linings of their airways. These changes don't signify a specific disease, but rather usually represent the body's response to stress or irritation. Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal (also known as retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably bet ...
deficiency or overdose can also lead to squamous metaplasia.
Uterine cervix
 In regard to the cervix, squamous metaplasia can sometimes be found in the
In regard to the cervix, squamous metaplasia can sometimes be found in the endocervix
The cervical canal is the spindle-shaped, flattened canal of the cervix, the neck of the uterus.
Anatomy
The cervical canal communicates with the uterine cavity via the internal orifice of the uterus (or internal os) and with the vagina via the ...
, as it is composed of simple columnar epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple columnar epithelium lines most organ ...
, whereas the ectocervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during ...
is composed of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium.Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; & Mitchell, Richard N. (2007) ''Robbins Basic Pathology'' (8th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 716-720
Significance
Squamous metaplasia may be seen in the context of benign lesions (e.g.,atypical polypoid adenomyoma
Atypical polypoid adenomyoma (APA) is a rare benign tumour of the uterus.
__TOC__ Pathology
APAs are characterized by glands with abnormal shapes that: (1) often have squamous metaplasia, and (2) are surrounded by benign smooth muscle. Nuclear a ...
), chronic irritation, ''or'' cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
(e.g., endometrioid endometrial carcinoma
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium (the lining of the uterus or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first sign is most o ...
), as well as pleomorphic adenoma.
See also
*Metaplasia
Metaplasia ( gr, "change in form") is the transformation of one differentiated cell type to another differentiated cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abno ...
*Dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic ...
*Barrett esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet ce ...
- a columnar cell metaplasia of squamous epithelium
*Subareolar abscess Also called Zuska's disease (only nonpuerperal case), subareolar abscess is a subcutaneous abscess of the breast tissue beneath the areola of the nipple. It is a frequently aseptic inflammation and has been associated with squamous metaplasia of la ...
References
{{pathology-stub Histopathology